
Research Topics
Perovskites solar cells: High yields have been achieved with perovskite cells, but their stability over time is low. Experimentally, it has been observed the inclusion of graphene in perovskite (MAPI)-based devices improved their stability. We are conducting a quantum-mechanical study of the effect on the electronic properties of the system caused by including graphene sheets. We use devices based on cesium and mixed composition perovskites that have experimentally shown promising values of photoconversion efficiency.

Adsorption phenomena on catalyst biomass derivatives.

Chemical sensors are devices that transform chemical information, ranging from the concentration of a specific component of the sample to the overall analysis of the composition, in an analytically useful signal. At molecular level, they are chemical systems, which can selectively bind analytes and provide information by modifying its physicochemical properties.

Dye sensitized solar cells are composed by a transparent conducting glass electrode covered with a film of porous nanocrystalline TiO2, where dye molecules are adsorbed to the semiconductor nanoparticles through substituents containing oxygen. A glass covered with platinum acts as the counter-electrode and an electrolyte containing the redox couple, e.g., I−/I3-, is immersed between the glassed.

Upon irradiation, the dye strongly harvests solar energy, gets photoexcited, and promotes the injection of electrons into the conduction band of the semiconductor. Before the charge recombination occurs, the oxidized sensitizer is regenerated to the native state by the electrolyte or a p-type hole conductor. The photocurrent is therefore generated by the injected charge, which passes through the external load to the counter-electrode and the circuit is completed by the reduction of e.g. I3-, which restores the I- ion.
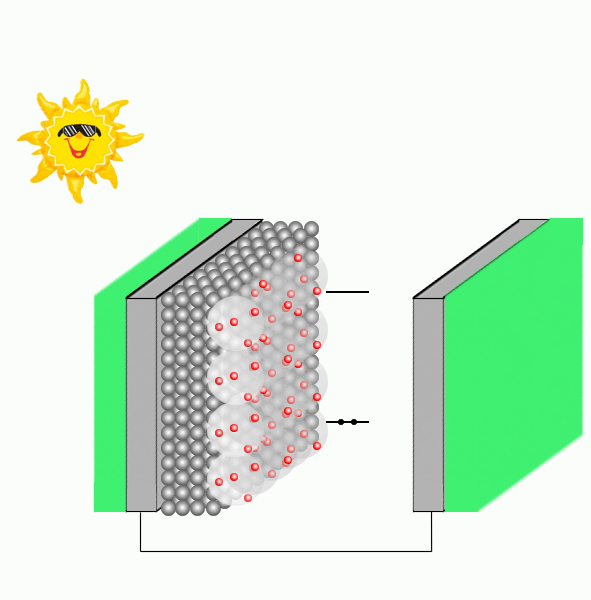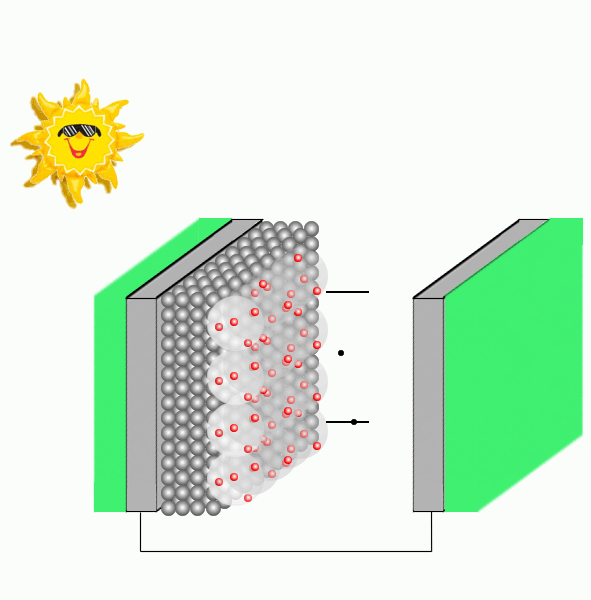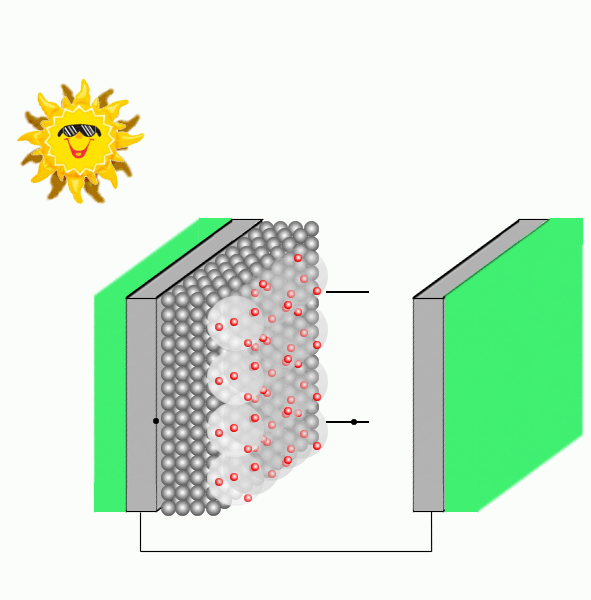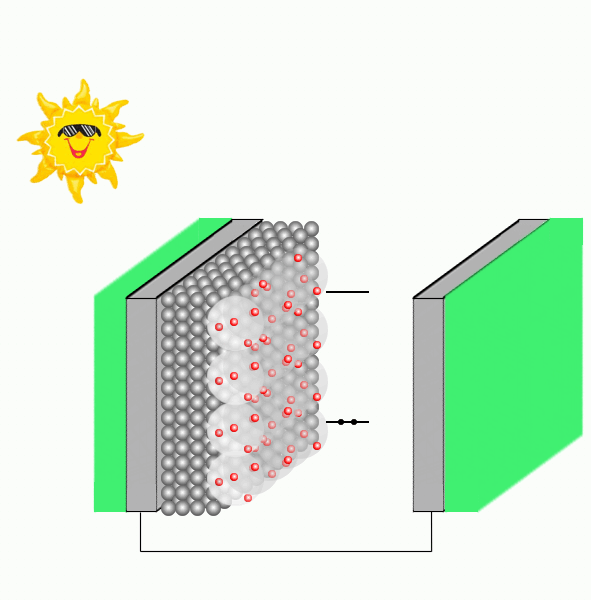
An important process in a DSSC performance is the electron photoinjection (PI) mechanism which can take place either via type I (indirect), that consists in injecting from the excited state of the dye to the semiconductor, or type II (direct), where the PI is from the ground state of the dye to the semiconductor upon photoexcitation.


The study of these topics is funded by the Grant Fondecyt 11140563 of the Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica CONICYT of Chile.
Curcumin and several analogs became the main subject of scientific research and there were discovered diverse biological properties, being the most important the anticancer activity using in vitro and in vivo models.
In this sense, the biological activity of these curcumin derivatives and substituted isoxazoles has made them an interesting focus for medicinal chemistry in the last few years. In fact, isoxazoles are potent, selective agonists at the human cloned dopamine D4 receptor2 and exhibit GABAA antagonist, analgesic, antiinflamatory, ulcerogenic, antimicrobial, antifungal, COX-2 inhibitory, antinociceptive and anticancer activities.

Organic solar cells are mainly composed by a donor and an acceptor material where the photocurrent generation process starts from absorbed photons resulting in excitons. These excitons diffuse in the donor-acceptor systems interface and then the hole electron pairs are disassociated into free charges which are transported by electrodes to collection.
The design of an efficient organic solar cell involves the optimization of the system at several levels, such as the light harvesting of the systems, viability of the hole electron pair generation, among others.
The development of new organic semiconductors with applications in photovoltaic devices has attached much attention in the last few decades. These semiconductors must accomplish a wide set of characteristics, for instance; a large charge–carrier mobility is important to decreasing the probability of recombination of charge–carrier, a large exciton diffusion length improves the number of excitons reaching the heterojunction and a low band gap allows a more extensive harvest of the solar emission spectrum

Liquid crystals combine the fluidity of liquids and the anisotropy of crystals, their main property is the charge transport through their structures which allow to these materials be components of several electronic devices like organic field-effect transistors, organic light-emitting diodes, organic photovoltaic cells, laptop screens, etc. Discotic liquid crystals (DLCs) are mesophases composed of rigid planar aromatic molecules containing several peripheral long alkyl chains. In this mesophase, the DLCs are quasi one-dimensional (1D) semiconductors because of the interaction between adjacent molecules, which form columns.
